Residues of gentamicin in the milk of cows eat mastitis
Know the causes, consequences, how to identify and also how to reduce gentamicin residues in the milk of cows diagnosed with mastitis
Por ser uma das enfermidades que mais acomete as vacas e interfere na qualidade do leite, é muito importante estar atento às causas da mastite. Assim, além de poder se precaver com relação à produção de leite, é possível atuar mais rapidamente no tratamento e de maneira assertiva.
However, this can be a challenge, especially for those who do not have the knowledge or rigor to supervise the herd. After all, it is not correct that dairy farmers only notice mastitis after its apparent symptoms. After identifying the disease, care must be taken with the next steps. It is possible that the treatment itself leaves some traces to be healed.
Para exemplificar, é possível pensar na aplicação incorreta ou demasiada de antibióticos como parte do tratamento de vacas com mastite clínica e subclínica. Nesses casos, os resíduos podem ser também modificadores do leite bovino.
Nesse artigo, você irá descobrir justamente o que acontece com os resíduos de gentamicina, qual a implicação deles para o leite, etc. Por isso, se você tem um rebanho para zelar e deseja ter sempre a melhor qualidade de leite possível, não deixe de fazer esta leitura!
To bring the content, the article was divided into the following topics:
- Mastitis as an antecedent problem to gentamicin residues
- Types of mastitis
- Application of antibiotics in response to mastitis
- Presence of antibiotic residues in cows' milk: cases of gentamicin
- How to properly administer gentamicin to avoid residues in milk?
- Why is it important to pay attention to gentamicin residues?
- How to identify the presence of gentamicin residues in the milk of cows treated with the antibiotic?
Mastitis as an antecedent problem to gentamicin residues
Os resíduos de antibióticos não aparecem por acaso. Na realidade, o seu surgimento deriva da intenção de sanar a mastite ou outras infecções nos animais. Porém a principal infecção que acomete o rebanho é a mastite, sendo responsável pela alteração da qualidade do leite, a quantidade do mesmo e também pela piora na saúde das vacas. Para entender mais sobre isso, confira os tópicos abaixo sobre a doença:
What is bovine mastitis?
Mastitis is characterized by inflammation in the mammary gland of cows. This disease results from a pathogenic microorganism that causes this infection after accessing the gland through the breast orifice or even through the blood.
As a consequence of this inflammation, there are physicochemical changes in cows' milk. These changes may vary with the type of mastitis (whether clinical or subclinical) and the level of severity of inflammation.
Types of mastitis
Clinical mastitis
In cases where animals in the herd are suffering from clinical mastitis, the producer will know. This is due to the fact that clinical mastitis presents visible symptoms, both in milk and in animals.
In case of inflammation, it is notorious that the udders are more tense and reddish, and it is common for them to become hotter than normal. This increase in temperature and pain in the breasts are great indicators that there is something wrong with the animal's mammary gland.
In milk, the changes come in the form of loss of quality. That's right, the changes are so expressive that the milk can have small globules, a curdled appearance or even the presence of pus.
For these reasons it is not possible to use the milk, which leads to tremendous waste.
Subclinical mastitis
This type of mastitis, in turn, does not require as much milk disposal. And although this seems like an advantage because you don't have to waste all the product, silent disease can be even more harmful to your herd.
After all, without showing symptoms, the disease spreads among cows. In these cases, if there is no supervision, you will only notice when the main factor of subclinical mastitis becomes visible: the decrease in milk production.
Application of antibiotics in response to mastitis
After identifying mastitis, the ideal is to start treatment as soon as possible. However, this treatment should not be arbitrary, that is, the antibiotic should be chosen correctly by the veterinarian and with adequate dosage.
After all, these drugs generate residues in the milk produced by the animal undergoing treatment. This means that the quality of the milk will also be at stake during the application of the medicines. And although there is no denying that antibiotics have scientific evidence and are efficient in curing mastitis, it is necessary to be very careful.
There are some factors to consider before applying the antibiotic:
- Accurate diagnosis of the disease;
- Adequate antibiotic prescription;
- Assertive dosage of the medicine.
These aspects are fundamental to guarantee the health of your animal, as well as the quality of the milk.
In this way, it is possible to reduce the effects of the medicine on the cows, and also to avoid antimicrobial residues in the milk. Furthermore, it is possible to avoid a major problem: antimicrobial resistance.
Presence of antibiotic residues in cows' milk: cases of gentamicin
In this context of treatment, a widely used antibiotic is gentamicin. This medicine is suitable for various bacterial infections, such as mastitis, and has intramammary action.
Sua administração exacerbada ou inadequada pode acarretar em resquícios no leite das vacas e causar alguns prejuízos. Entre eles: a alteração na microbiota do leite e o consequente perigo da resistência bacteriana em humanos. Além da questão de que se o leite estiver com resíduos acima do limite permitido em legislação, ele se torna impróprio para consumo, devendo ser descartado.
But how does this happen?
Well, the alteration of the microbiota occurs from the reactions that the residues cause in the lactic bacteria. By itself, this alters the fermentation of the milk.
From transmission to humans, although the antibiotic is present in small concentrations, in larger quantities or with recurrent consumption, there may be serious damage, such as the resistance of microorganisms or even the death of beneficial intestinal bacteria.
After all, it is worth mentioning that gentamicin, for example, is also a medicine for human use, prescribed to fight bone, joint and urinary tract infections. In addition to other inflammations, such as in the pelvis, meningitis, pneumonia, etc.
Therefore, gentamicin residues in milk can lead to several weaknesses in relation to the development of these diseases. This becomes even worse when relating the danger to pregnant women.
For this reason, there are studies that investigate gentamicin residues in milk, their variation, as well as the concentration limit for these residues.
How to properly administer gentamicin to avoid residues in milk?
It is important to know the correct way to apply the antibiotic. So, here are some application tips:
Correct dosage
The correct dosage of gentamicin and antibiotics as a whole is essential to avoid all the aforementioned factors, in addition to economics.
Thus, both the abusive and insufficient use of gentamicin can be a problem, because while the first can generate large concentrations of residues, the second can promote bacterial resistance and delay healing.
Correct application of the medicine
In addition to diagnosis, identification of the antibiotic, and proper dosage, it is important that administration be accurate. Mainly in cases of intramammary administration, in which the udder is exposed and is quite sensitive.
In these cases, the region needs to be cleaned with alcohol and the insertion object must be new and sterilized. It is worth mentioning this because people without knowledge can use a single cannula to administer the antibiotic in different cows.
However, this is strictly prohibited. After all, the udders are hotbeds of bacteria and can end up transmitting them to other animals through the cannula. Therefore, it is important to change gloves during applications as well.
Have professional support
Both to get the dosage of the antibiotic right and to choose it, as well as to have the correct diagnosis, it is essential to have the support of a veterinarian.
In addition, the correct application is also the responsibility of those who have knowledge and are able to do so.
This professional, in fact, must be on hand to supervise his herd and take care of the health of the cows.
And in the administration of antibiotics, it is fundamental that he is the manager. In this way, it is possible to have the experience and knowledge necessary to have a good job.
Why is it important to pay attention to gentamicin residues in cow's milk?
As seen, there are some essential precautions during the application of antibiotics, such as gentamicin. These precautions are important to reduce antibiotic residues in milk production.
Estudos realizados por Thamires Martins (2013) com o objetivo de analisar a presença de resíduos de antibiótico no leite, apontou que ao menos 24,95% das amostras tiveram resultado positivo. E esse número foi resultado de uma análise após 9,3 dias da aplicação do medicamento.
This means that during all these days milk production, the effects of gentamicin will still be present in milk production. And, as seen, there are several consequences of these residues to the cow, to the quality of the milk and consequently to the consumer population.
The latter, in turn, has increasingly valued healthy and alteration-free foods. In this sense, milks with gentamicin residues, even if only as a result of a temporary treatment of clinical or subclinical mastitis, can be fatal for your business.
Therefore, there is little detail around the quality and production of the milk. Thus, an adequate way to guard against this risk is to separate not only cows with mastitis, but also those undergoing antibiotic treatment.
This may make it possible to monitor milk composition as well as prevent gentamicin residues from being present in all dairy production. With the help of a professional and a lot of information, it is easier to have quality milk, as well as less loss in production.
Além disso, é preciso estar atento à validade do antibiótico (que infere sobre os resíduos deixados) e à quantidade correta, sendo possível assim produzir leite dentro dos
Limites Máximos de Resíduos, determinados na legislação brasileira.
How to identify the presence of gentamicin residues in the milk of cows diagnosed with mastitis?
After the application of the drug, it is highly recommended that the cows be supervised. This means both your immune response and the condition of the milk.
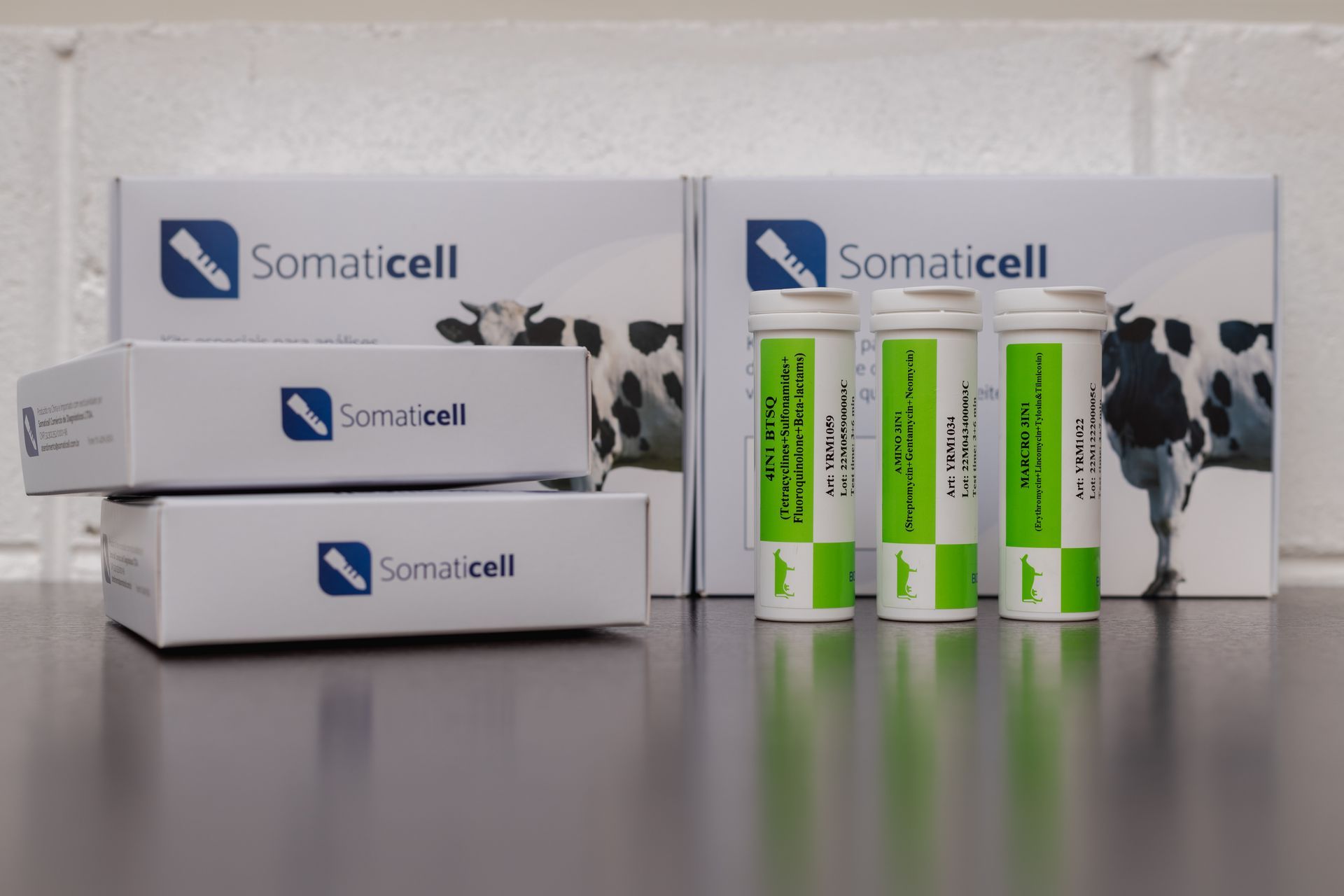
E para ter certeza se existem resíduos do medicamento presentes na produção do leite, é sempre possível contar com os testes da Somaticell. Trabalhamos com análises para todas as famílias de antimicrobianos exigidas na legislação brasileira, sendo possível analisar se o leite pode ser comercializado ou não.
After all, with years in the market and the necessary experience to care for its herd, the company could not be left out of the identification of antibiotic residues.
Por isso, em casos de gentamicina, o teste adequado é o kit Amino 3IN1, um teste direcionado à família dos aminoglicosídeos.
This test uses colloidal gold immunochromatography technology, resulting in a clear, precise and safe analysis. This is ensuring the certainty you need to identify the presence of gentamicin residues.
In addition, the test has many advantages such as:
- Fast and accurate results in 8 minutes;
- Smaller margin of error in the analyses;
- Lower milk disposal (sensitivities closer to Brazilian standards, allowing safe milk processing without unnecessary disposal);
- Can be used in the laboratory or in the field;
- Visual interpretation or via bluetooth reader (consigned);
- No heating or cooling required;
- Negative and positive controls, ensuring the quality of the analyses;
- Online Technical Support - 24/7 and others.
Por isso, se você deseja verificar a existência de resíduos de gentamicina no leite de vacas com diagnóstico de mastite clínica ou mesmo subclínica, conte com o
kit Amino 3IN1!
Gostou do nosso conteúdo? Saiba que no blog da Somaticell é possível encontrar muito mais informações acerca de como manter a saúde do seu rebanho e como melhorar a qualidade do seu produto através do bom manejo da ordenha!
We are a company that aims to help you and your business to obtain better solutions and results!
Portanto, não deixe de conferir outros artigos e entrar em
Contact conosco!

Conheça nosso App

Our Educational Videos
Somaticell on Social Networks