Reagents for chemical analysis of milk
No time to read? Listen to the narration of this article in Portuguese:
What are chemical analyzes of milk?
Behind every drop of milk, there are a series of rigorous tests and analytical processes. Although the Somaticell has established itself in the market as a leading supplier of reagents and chemical solutions, its story is not just about products, but about the passion for precision and reliability.
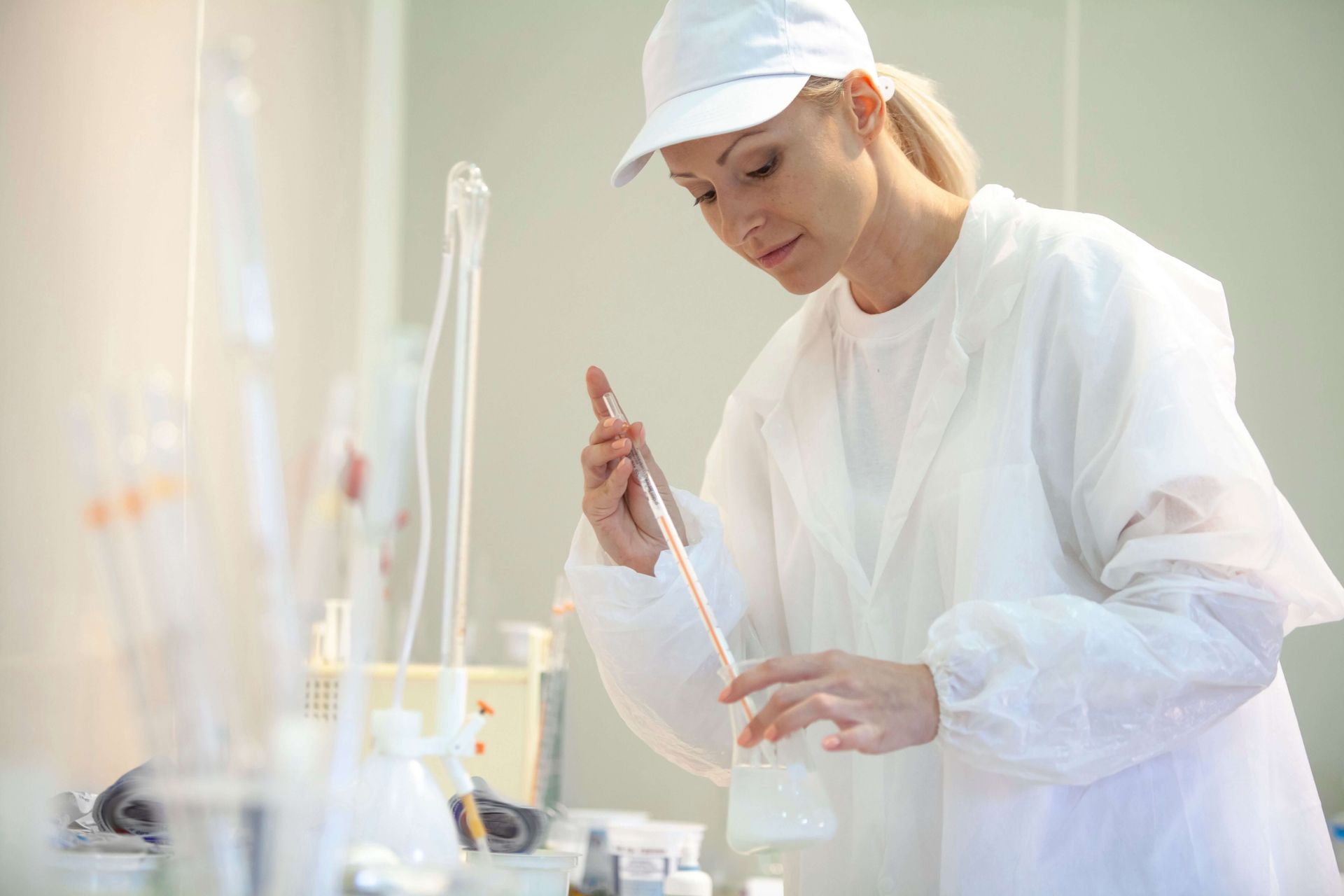
Within the sterile walls of a laboratory, reagents are like unsung heroes. Especially when we talk about milk and dairy products, precision is crucial. Imagine the challenge of detecting impurities or adulterations in a substance as complex as milk! And this is where the Somaticell shines.
Let's explore together the wonderful world of milk chemistry and understand how quality reagents take our eating experience to a higher level.
The main chemical analyzes carried out on milk
In an era of increasing awareness about health and wellbeing, understanding the exact composition and quality of the food we consume has become of paramount importance. When we talk about milk, a fundamental food in many diets around the world, this need becomes even more pronounced.
Milk is a complex tangle of nutrients, each with its specific properties and functions. Therefore, to ensure its purity, quality and integrity, a series of meticulous chemical analyzes are carried out.
Next, we will delve into the universe of chemical analyzes associated with milk, exploring the different tests, their purposes and how they are carried out. For producers, these tests guarantee product consistency and quality. For consumers, they provide confidence that they are consuming a safe and nutritious product.
Silver Nitrate Solution
- This solution is used in a titration to determine the concentration of chlorides in milk. The excessive presence of chlorides may indicate mastitis, an inflammation of the mammary gland. It is also used to determine the concentration of salt (sodium chloride) in dairy products. The reaction involves the formation of insoluble silver chloride and the end point of the titration is usually detected by means of an indicator (Potassium Chromate) or by a change in electrical potential (automated titration)
Deionized and Demineralized Water
- Deionized water is purified by removing its impurities and mineral ions through an ion exchange process. Demineralization is a complementary process and refers to the complete removal of minerals, given that, in laboratories, water purity is crucial to avoid interference with chemical reactions. Water is often used as a solvent for preparing other solutions.
Cryoscopy Reagents
- A crioscopia mede o ponto de congelamento do leite é o único método que não pode ser substituído e deve seguir rigorosamente o método oficial descrito nas metodologias do MAPA. O leite adulterado com água terá um ponto de congelamento diferente do leite puro. A crioscopia usa o crioscópio que só pode ser calibrado adequadamente utilizando os padrões oficiais. O ponto de congelamento é detectado pelas variação da quantidade de sólidos.
Alizarol Test
- The alizarol test evaluates the acidity of milk by varying the color of this indicator: -Acidic milk yellow -Alkaline milk purple -Normal milk pink. When using alizarol dissolved in ethyl alcohol (ethanol), the milk will have good quality if it does not coagulate, and the milk will be resistant to the alcohol content used. The minimum alizarol test standard is used at 72 GL degrees. A Somaticell has Alizarol in all alcohol levels normally used in dairy products.
Peroxide Test
- This test evaluates the quality of milk by detecting the presence of peroxides in milk. In an acidic solution, milk peroxide reacts with an indicator producing a colored reaction, indicating that this preservative is present in the milk.
Reagentes para a Análise de Proteínas
- The protein content of milk is often determined by the Kjeldahl method, which involves mixing the sample, distillation and titration. This method quantifies the total amount of nitrogen, which is then used to estimate the amount of protein (considering that proteins are the main source of nitrogen in milk).
Fat Determination
- The fat content of milk is commonly determined by the Gerber method, which involves the addition of sulfuric acid and isoamyl alcohol. The mixture is centrifuged and the separated fat layer is measured. The amount of fat influences properties such as flavor, viscosity and caloric content of the milk.
Alkaline Phosphatase Tests
- The presence of alkaline phosphatase indicates that pasteurization was not effective. Alkaline phosphatase is inactivated at pasteurization temperatures, so if it is present, it suggests that the milk has not been properly pasteurized. The test involves incubating milk samples with a specific substrate and measuring the release of p-nitrophenol, which is yellow and can be measured spectrophotometrically.
The Crucial Quality of Reagents in Milk Analysis
In the world of analytical chemistry, the quality of the reagent is a fundamental pillar. In the analysis of milk, this is no different. Let's understand why reagent quality is so critical and how it can affect the dairy production process.
- Identificação da Qualidade do Reagente: A primeira etapa é saber como identificar um reagente de alta qualidade. Há várias características a se considerar:
- Pureza: A composição pura garante que não haja contaminações que possam interferir na análise.
- Rótulo claro: Informações claras sobre a composição, data de validade e condições de armazenamento são essenciais.
- Certificado de análise: Um reagente deve vir com certificados que validam sua qualidade, composição e que garantam a qualidade
Impacts of Low Quality Reagents:
The use of inferior quality reagents can have serious consequences:
- Resultados Inconsistentes: A confiabilidade dos resultados é prejudicada, levando a análises errôneas.
- Aumento dos Custos: Pode ser necessário repetir os testes, levando a um uso maior de recursos.
- Prejuízo à Imagem: Produtos defeituosos no mercado podem prejudicar a imagem do produtor de laticínios.
Keeping an eye on quality:
When purchasing reagents, pay attention to the following points: Check whether they were produced to meet the reference method. Requesting samples and carrying out tests to ensure that your reagents are in accordance with official specifications are best practices adopted worldwide.
The Excellence of Somaticell in the Production of Reagents for the Dairy Industry
A Somaticell, through years of dedication and research, has consolidated its position as a leader in supplying high-quality reagents and chemical solutions to laboratories across the country. But what makes your products so special? The answer lies in the precision, purity and reliability they provide.
A Somaticell is also dedicated to educating its customers on the correct use of these products. Workshops, seminars and training are regularly offered to ensure laboratories obtain the best possible results with the reagents provided.
Conclusion
The chemical analysis of milk is a crucial step to guarantee the safety and quality of this food that is widely consumed worldwide. From checking for antibiotic residues to in-depth analysis of its nutritional profile, each test contributes to the trust we place in every drop of milk. The quality of the reagents plays an undeniable role in this process.
As science advances, the accuracy and depth of these analyzes will only improve, ensuring a safer and more beneficial product for everyone.


Discover our App

Our Educational Videos
Somaticell on Social Networks